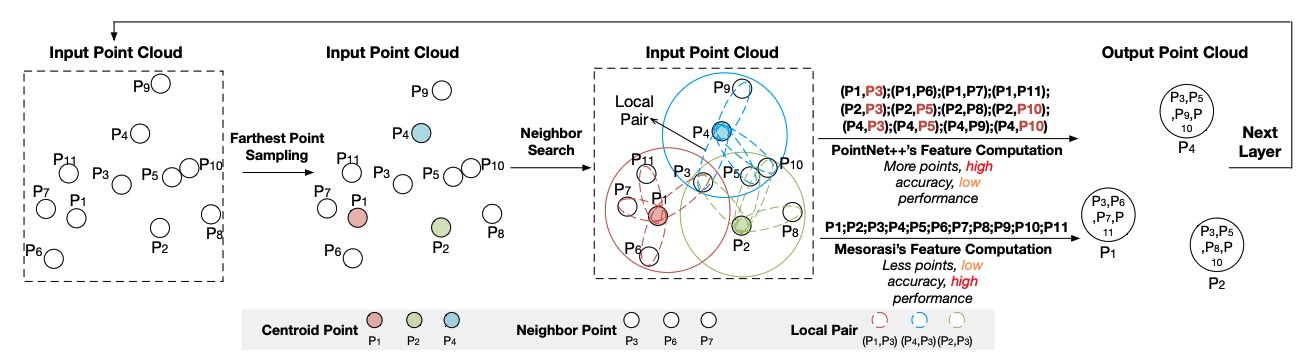
Recent point cloud recognition (PCR) tasks tend to utilize deep neural network (DNN) for better accuracy. Still, the computational intensity of DNN makes them far from real-time processing, given the fast-increasing number of points that need to be processed. Because the point cloud represents 3D-shaped discrete objects in the physical world using a mass of points, the points tend for an uneven distribution in the view space that exposes strong clustering possibility and local pairs’ similarities. Based on this observation, this paper proposes PRADA, an algorithm-architecture co-design that can accelerate PCR while reserving its accuracy. We propose dynamic approximation, which can approximate and eliminate the similar local pairs’ computations and recover their results by copying key local pairs’ features for PCR speedup without losing accuracy. For accuracy good, we further propose an advanced re-clustering technique to maximize the similarity between local pairs. For performance good, we then propose a PRADA architecture that can be built on any conventional DNN accelerator to dynamically approximate the similarity and skip the redundant DNN computation with memory accesses at the same time. Our experiments on a wide variety of datasets show that PRADA averagely achieves $4.2\times$, $4.9\times$, $7.1\times$, and $12.2\times$ speedup over Mesorasi, V100 GPU, 1080TI GPU, and Xeon CPU with negligible accuracy loss.
Authors: Zhuoran Song, Heng Lu, Gang Li, Li Jiang, Naifeng Jing and Xiaoyao Liang.